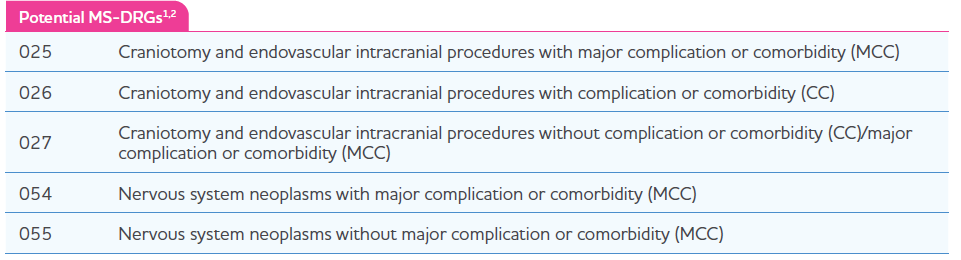
Medicare Severity Diagnosis Related Group (MS-DRG) Coverage
Similar to other inpatient administered drugs, Gleolan® will be bundled by payers into hospital payment rates (ie, MSDRGs), all patient refined (APR DRGs), or other DRGs specific to the individual payer’s internal methodology. DRG assignment depends on the diagnosis and the craniotomy or craniectomy procedure with which Gleolan will be bundled. Medicare utilizes MS-DRGs; the 5 MS-DRGs that represent craniotomy or craniectomy treatments involving Gleolan are shown in the table below. This table may not be reflective of all MS-DRGs or other non–MS-DRGs that may be used for Gleolan. Only 1 MS-DRG should be assigned to a patient for a particular hospital admission.
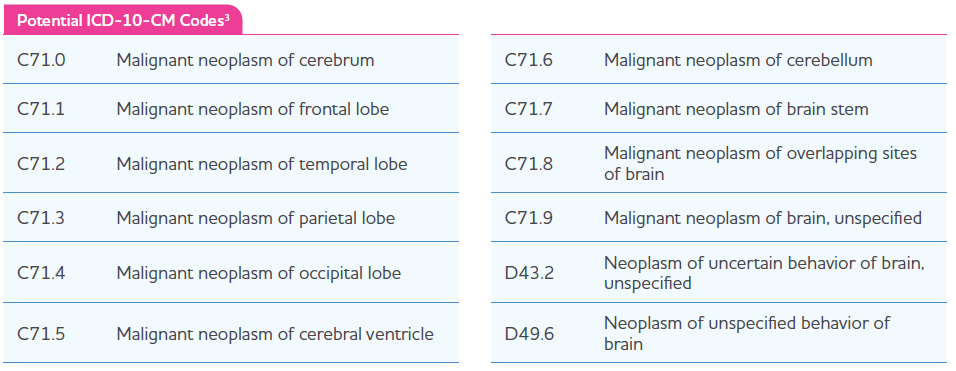
ICD-10 Clinical Modification (CM) Diagnosis Codes
Hospitals use current ICD-10-CM codes to report a patient’s diagnosis on claims forms. Correct coding is the responsibility of the hospital submitting a claim for the item or service. Always check payer guidelines to verify diagnosis coding requirements as individual payer rules may vary and must be adhered to. Below is a range of potential ICD-10-CM diagnosis codes that may be related to a diagnosis within Gleolan’s approved label.
ICD-10 Procedure Coding System (PCS) and Revenue Code
Effective 01/01/2019, the Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services (CMS) created a new PCS code that captures the PCS method value Fluorescence Guided Procedure and the PCS qualifier value Aminolevulinic Acid and applies them to the fourth character body region values and applicable approaches. These changes enable the capture of additional detail for fluorescence-guided procedures that use aminolevulinic acid. The ICD-10-CM/PCS Coding Clinic Fourth Quarter 2019, pages 41 to 42, confirms the utilization of code 8E090EM for Fluorescence Guided Procedure of Head and Neck Region Using Aminolevulinic Acid, Open Approach. For additional information, please consult the current ICD-10-PCS manual. Some individual payers may require specific accommodations for billing imaging agents on inpatient claims. Always confirm adherence to specific payer rules and guidelines.

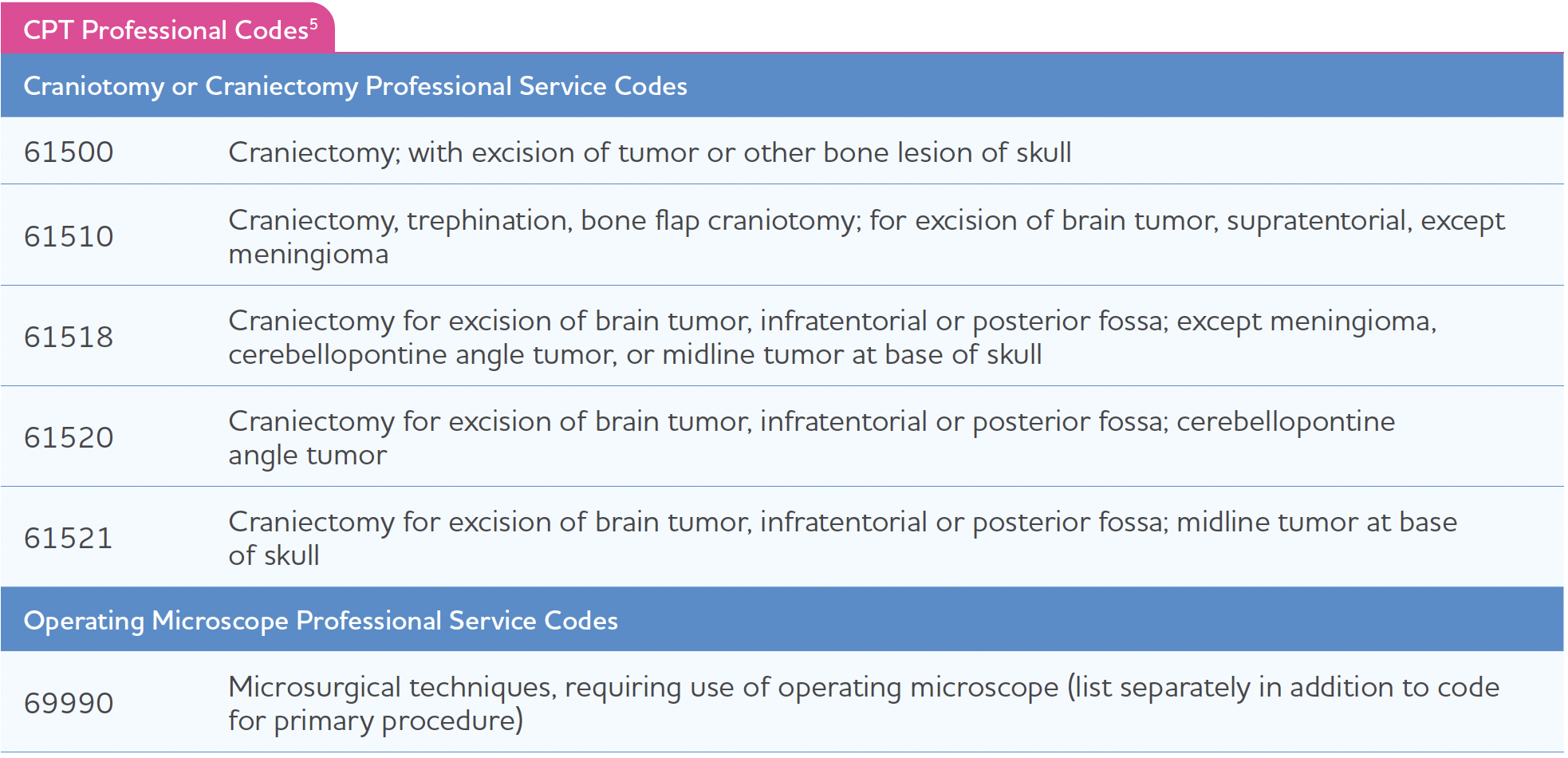
Professional Current Procedural Terminology (CPT) Codes
In addition to facility inpatient reimbursement, some hospitals also bill out professional physician fees separate from the inpatient procedure. Craniotomy and craniectomy procedures will vary. The below list is meant to serve as a guide of commonly used professional fees; however, it is not exhaustive, and individual circumstances and payer rules will determine coding.
Each payer can have unique requirements for their claims process. Please consult with the payer to ensure compliance with their requirements.
Obtain more information on reimbursement support by calling 1-833-433-9833, from 9:00 am to 5:00 pm EST Monday through Friday (excluding holidays).
Important Safety Information
Contraindications
Do not use Gleolan in patients with:
- hypersensitivity to aminolevulinic acid (ALA) or porphyrins
- acute or chronic types of porphyria
Warnings and Precautions
Due to the risk of phototoxic reactions, do not administer phototoxic drugs and topical preparations containing ALA for 24 hours during the perioperative period. Reduce exposure to sunlight or room lights for 48 hours after administration of Gleolan.
Errors may occur with the use of Gleolan for intraoperative visualization of malignant glioma, including false negatives and false positives. Non-fluorescing tissue in the surgical field does not rule out the presence of tumor in patients with glioma. Fluorescence may be seen in areas of inflammation or metastases from other tumor types.
Hypersensitivity reactions, including serious hypersensitivity reactions have occurred; these reactions include anaphylactic shock, swelling, and urticaria. Always have cardiopulmonary resuscitation personnel and equipment readily available and monitor all patients for hypersensitivity reactions.
Adverse Reactions
Adverse reactions occurring in >1% of patients in the week following surgery were pyrexia, hypotension, nausea, and vomiting.
Nervous system disorders occurred in 29% of patients within the first week after surgery and events occurring in >1% of patients included: aphasia (8%), hemiparesis (7.8%), hemianopsia (3.2%), headache (2.7%), seizure (1.9%), hemiplegia (1.9%), monoparesis (1.3%) and hypoesthesia (1.1%). Brain edema occurred in <1% of patients in the first 6 weeks after surgery. In a randomized clinical trial, the numbers of serious neurologic adverse events in the post operative period were higher in patients randomized to ALA fluorescence arm compared to the control arm. An imbalance was notable for the adverse events aphasia, ataxia, convulsion and hemianopsia and is likely related to the higher amount of brain resection performed in the ALA arm. At longer follow up periods, the numbers between the two arms appeared similar.
Worsening of >2 Common Toxicity Criteria grades in alanine aminotransferase and gamma-glutamyl transferase occurred in 15.8% and 11.6% of patients, respectively, within the first week after surgery. Absolute levels ranged from 2 times to greater than 10 times the upper limit of normal for each parameter. At 6 weeks, these measurements remained elevated in 2.9% and 7.5% of patients, respectively. There were no cases of liver failure.
Drug-Drug Interactions
See information under Warnings and Precautions regarding phototoxic reactions.
Please see Full Prescribing Information
For medical inquires, please fill out our Medical Information Request Form.