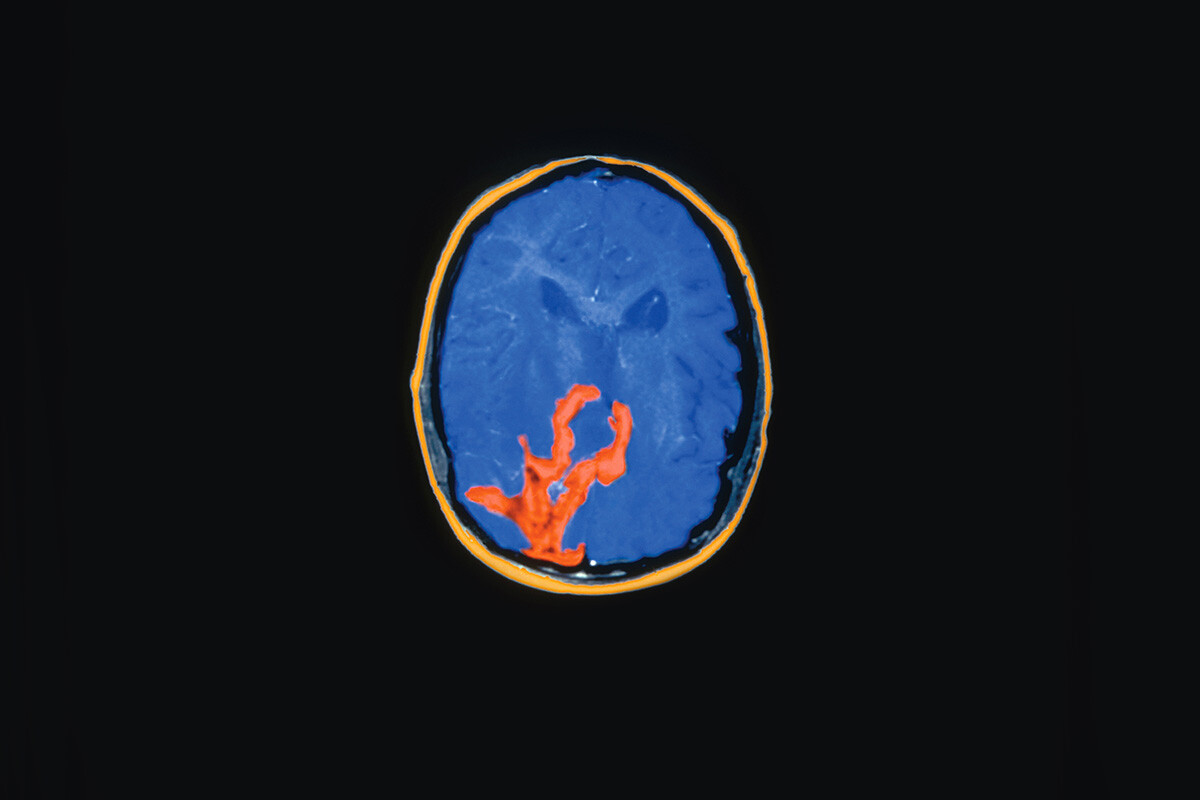
What Are Malignant Gliomas?
Malignant gliomas are the most common type of primary malignant brain tumor. These World Health Organization (WHO) Grade III or IV tumors include1:
- Glioblastoma multiforme (GBM)
- Glioblastoma multiforme (GBM) is the most common brain tumor in adults. GBM is a primary brain tumor, which means it originates in the brain tissue.
- On average, more than 12,000 glioblastoma cases are diagnosed each year in the US.
- Anaplastic ependymoma (AE)
- Anaplastic astrocytoma (AA)
- Anaplastic oligendroglioma (AO)
- Pineoblastoma
How Are Malignant Gliomas Treated?
There are a variety of approaches to treating malignant gliomas, including surgery, radiation therapy, and chemotherapy. Healthcare providers advise patients on treatment based on the type and grade of brain tumor, its location and size, and the patient’s age and health1.
Removing the Tumor During Surgery
As part of your treatment plan, your neurosurgeon will be performing surgery to remove as much of your tumor as they can safely remove. This is known as “resection.” The amount of tumor that can be removed is determined by the tumor’s size and location. The goal is to remove as much of the tumor as possible without harming areas of the brain that control critical functions such as speech or balance. Gliomas generally have very small cells that grow into brain tissue, which may make it difficult to see and resect1,2.
REFERENCES
1. About brain tumors. American Brain Tumor Association. https://www.abta.org/about-brain-tumors. Published May 26, 2022. Accessed August 2, 2022.
2. Data on file. NX Development Corp.
Patient Safety Information
Gleolan can cause a sunburn-type skin reaction, also referred to as photosensitivity. Do not take any drugs that may worsen this (such as St. John’s wort, griseofulvin, thiazide diuretics, sulfonylureas, phenothiazines, sulphonamides, quinolones, and tetracyclines) and do not put anything on your skin that contains aminolevulinic acid (ALA) for 24 hours before and for 24 hours after receiving Gleolan.
Errors may occur with the use of Gleolan to see tumors. Sometimes brain tumor cells may fluoresce even if they are not cancerous or those that are cancerous my not fluoresce. Also, cancer cells from other tumors or areas of swelling may fluoresce.
Allergic reactions, including serious allergic reactions, to Gleolan have occurred. Your medical team should monitor you for this and should have emergency equipment ready to manage any such reaction if it occurs.

Patient Safety Information
Gleolan can cause a sunburn-type skin reaction, also referred to as photosensitivity. Do not take any drugs that may worsen this (such as St. John’s wort, griseofulvin, thiazide diuretics, sulfonylureas, phenothiazines, sulphonamides, quinolones, and tetracyclines) and do not put anything on your skin that contains aminolevulinic acid (ALA) for 24 hours before and for 24 hours after receiving Gleolan.